Unexpected Results From a Major Study, Is It Worth Doing?
Although many view a colonoscopy as an uncomfortable or even scary procedure, 17.7 million of them are carried out annually in the United States, and 60.6 percent of people have had one in the past 10 years.
It’s believed that a colonoscopy not only helps find cancer but also prevents cancer from developing from polyps. Because of its high level of sensitivity and specificity, colonoscopy has been regarded as the gold standard for colon cancer screenings for a long time.
Unexpected Result From a Major Colonoscopy Study
However, a recent major clinical study, the Nordic-European Initiative on Colorectal Cancer (NordICC) study published in October 2022, raised questions about the efficacy of colonoscopy.
The study suggested that colonoscopies don’t save as many lives as previously thought.
Researchers recruited 84,585 participants in Poland, Norway, Sweden, and the Netherlands; 28,220 were in the invited group (invited to do colonoscopy), and 56,365 were in the usual-care group.
At the end of the 10-year follow-up, the risk of colorectal cancer-related death at 10 years was 0.28 percent among participants in the invited group and 0.31 percent in the usual-care group. The risk of death from any cause was 11.03 percent in the invited group and 11.04 percent in the usual-care group.
In terms of adverse events, 15 people had major bleeding after polyp removal. According to the study, there were no screen-related deaths within 30 days after colonoscopy.
The incidence of colon cancer has dropped significantly since 1975. Most people believe this is due to increased screening and improved treatment.
Since there were no randomized clinical trial data on colonoscopy for colorectal cancer before, the NordICC trial sparked a heated discussion: Can colonoscopy truly prevent colon cancer?
If the benefit is not what people have expected, the colon cancer-screening landscape could be totally reshaped.
The Study Invokes Intense Debate
Numerous doctors argue that NordICC’s researchers should maintain follow-up in their study, and assessments of other current trials may shed light on the advantages of screening colonoscopies after 10 years. Follow-up time is very important, as many believe the benefit of a colonoscopy is treating precancerous polyps. It may be decades before we see the long-term benefit of colonoscopy screening.
Doctors perceive the results of the NordICC study differently for the following reasons.
First, the trial had lower-than-expected participation—only 42 percent underwent colonoscopy—and provides no information on adherence to guidelines for polyp surveillance.
Most think the study doesn’t change the value of colonoscopy. The test would have lowered cancer risk by 31 percent and cut the probability of dying from colorectal cancer by 50 percent if compliance had been 100 percent, according to the research findings.
Also, the tested countries have a higher mortality rate and incidence rate compared to the United States. U.S. clinicians favor colonoscopy, while European health systems rely far more on flexible sigmoidoscopy, which only examines the lower part of the colon.
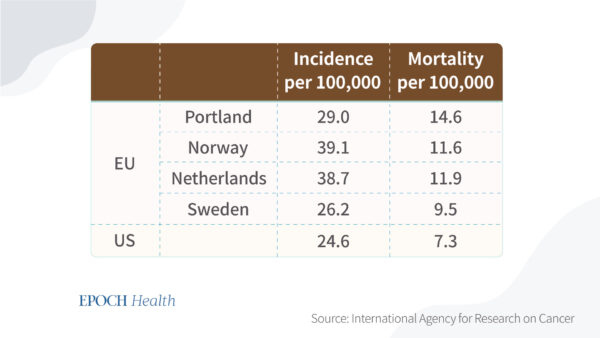
However, countries without screening programs still witnessed improvements in colorectal cancer mortality. A comment on the findings published in The Lancet Oncology stated that firm conclusions cannot yet be drawn on the causal relationship between colon cancer mortality and national screening.
Second, the operator affects the colonoscopy’s effectiveness. The adenoma detection rate is the percentage of screening colonoscopies in which one or more adenomas are found.
Patients are better protected from adenoma development by endoscopists with higher adenoma detection rates.
Third, the study was done among European populations and may not be representative of the various demographics in the United States.
The Risks of Colonoscopy
The benefits and risks depend on compliance with the screening protocol, the chance of meeting with an experienced endoscopist, and your own risk of developing colon cancer.
For a person with a family history, it might be more beneficial to keep a close look and a healthy diet.
On the other hand, a healthy lifestyle doesn’t guarantee that you won’t have colorectal cancer. First-degree relatives of people with colorectal cancer are at a sixfold increased risk of colon cancer before 50 years old. Second- and third-degree relatives correspond to one-and-a-half and three times increased risk, a two- to threefold increased risk of colorectal cancer.
A doctor may determine you’re at high risk if you have a family history of colon cancer or you have a history of colon polyps or inflammatory bowel disease.
Colonoscopy is still the golden standard if the patient is suspected of cancer. And it will benefit patients most if a cancer is found and removed in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (the development of cancerous change in a dysplastic polypoid lesion).
The prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer varies according to the site of cancer, with right-sided tumors having the most severe prognosis, making early diagnosis in this group of patients especially important.
However, there are many risks for colonoscopy—in addition to the risk of sedation.
Risks of colonoscopy include major bleeding (14.6 events per 10,000 performed), perforation (3.1 per 10,000), or even infection. These rates are higher than in sigmoidoscopy, a less expensive, less invasive method that can be performed without sedation.
Colonoscopy is more invasive and burdensome than other colon cancer tests such as fecal testing and sigmoidoscopy, and it requires more clinical resources.
A few medical organizations have dropped the recommended age to begin colorectal cancer screening from 50 to 45. The reason for this is that scientists are striving to learn more about the causes, the biology, and how to prevent the illness from developing earlier in life. Several risk factors have become more prevalent over the past 45 years, such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and smoking, which can lead to more instances of early-onset cancers. Poor diet, particularly one high in processed meat and fat and low in fruits and vegetables, is increasingly being linked to early-onset colorectal cancer. Several studies have also discovered that being overweight or obese may increase one’s risk of developing colorectal cancer with early onset.
Since colorectal cancer is still relatively rare, affecting less than 1.8 per 100,000 younger adults (below age 40), lowering the screening age might be a burden and not cost-effective. In addition, the trend of new young patients might be because of early screening and overdiagnosis, which could further burden the person.
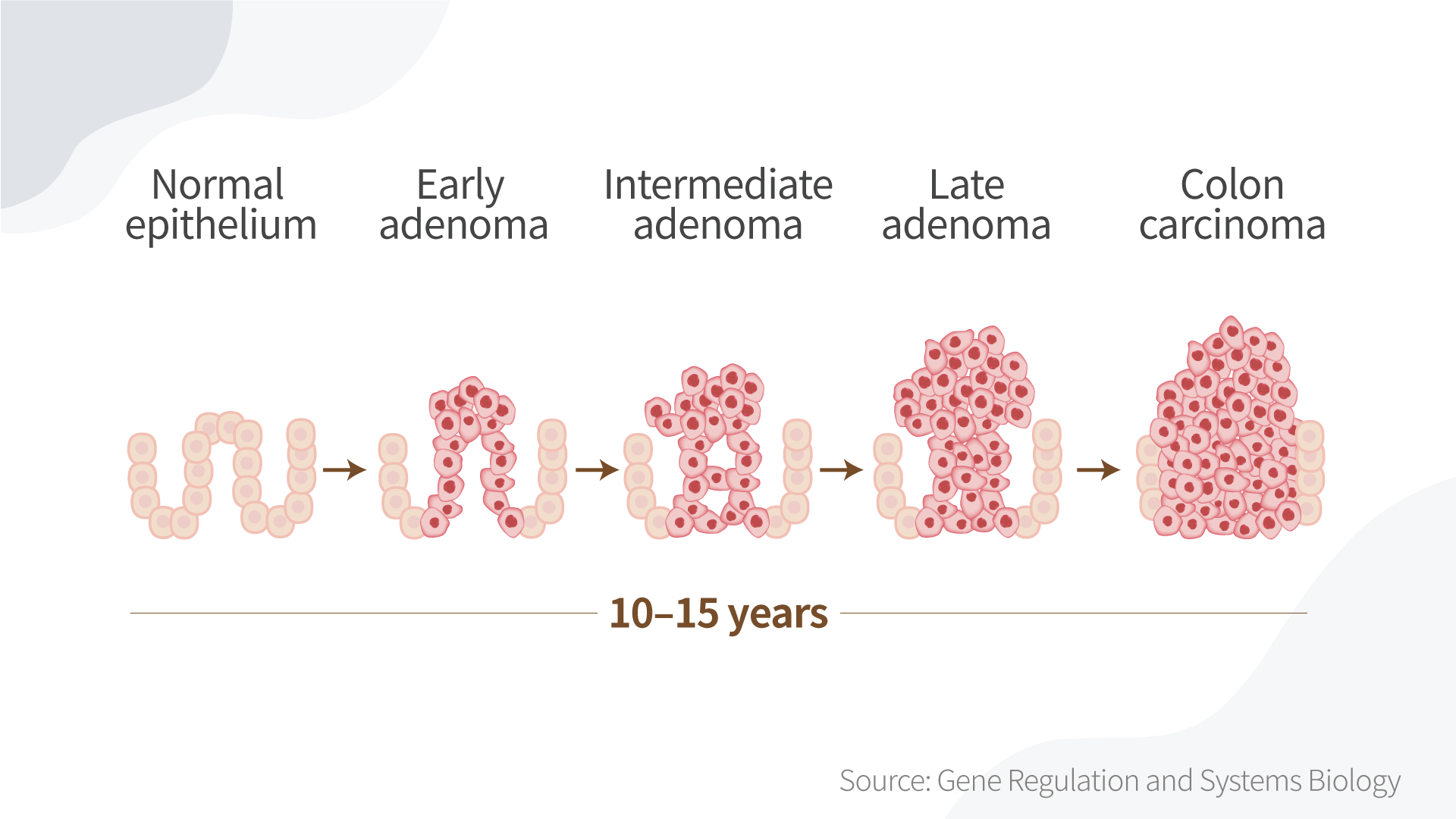
The below figure shows the long process of colon cancer development. If the in situ cancer is identified very early, the five-year survival rate may improve. But no one can really tell how long it takes for a cancer cell to grow into something lethal, and there are other risks to consider that may affect outcomes, as well.
Weigh Both Sides
Deciding whether it is cost-effective to do a colonoscopy will be based on your own risk of developing colorectal cancer, depending on your family history and other risk factors.
If you develop severe bleeding due to receiving an endoscopy, harm is 100 percent likely. To avoid the chance of harm, or if you can’t tolerate colonoscopy, some studies have proved that a fecal immunochemical test for screening patients at increased risk for colorectal cancer has high overall diagnostic accuracy, given its safety, simplicity, low cost, accuracy, and minimal discomfort.
We still need better data on colonoscopy’s benefits and risks. To account for comorbidities, oncological treatments, stage-related differences at the time of diagnosis, family history, and other risk factors, additional in-depth patient-level data are required.
Ideally, a patient would use a digital pathology tool, and then his doctor would provide him with information. For example, “Mr. Smith, your chance of getting colorectal cancer is X percent based on all the information you’ve provided, and Y percent of people like you get a colonoscopy at your age. For you, it can decrease Z percent of the risk of colon cancer.”
However, there are many uncertainties in life. Even in the way you cook, what ingredients you use, and how they were processed—it is hard to digitize such factors, as there is no single model to predict a person’s risk. Tailoring colorectal cancer screening approaches to each person based on their risk factors and precision screening may improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of colonoscopy screening.
Views expressed in this article are the opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of The Epoch Times. Epoch Health welcomes professional discussion and friendly debate. To submit an opinion piece, please follow these guidelines and submit through our form here.




